SAARC
SAARC is the abbreviation of the
South Asian Association for Regional Co-operation. It is a voluntary
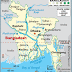
association of the eight countries including Maldives, Nepal, Bangladesh,
India, Pakistan, Bhutan, Sri-Lanka, and Afghanistan. Its main aim is to fight
against poverty and to work in co-operation in different sectors.
SAARC was formed in 1985 with
Bangladeshi President Ziaur Rahman as its main initiator. The Secretariat is
located in Kathmandu, Nepal.
Its first conference was held in
1985 in Dhaka. Its first chairman was Mohammad Ershad and the first
secretary-general was Abul Ahsan.
Maldives has one of the highest
literacy rates among SAARC countries. The landlock countries included in SAARC
are three (Afganistan, Nepal, and Bhutan).
There are many similarities
between these eight countries in their people and they're socio-economic
conditions. Again, they are different from each other in population, size,
resources, level of development, and form of government. These countries are
associated with SAARC so that they can co-operate with one another in different
sectors like trade and commerce, agriculture, science and technology, and
exchange of knowledge. They can work together to improve their standard of
living.
SAARC agreements: SAPTA (1993),
SAFTA (2004).
We hope that SAARC can ensure
progress and prosperity and a better life for all.






No comments